Shareholder Meeting
This guide will walk you through the essential elements of use shareholder meeting to keep your attendees aligned and engaged.
Try Lark for Free
Shareholder meetings play a critical role in upholding transparency and communication within an organization, allowing stakeholders to engage in crucial decision-making processes. With the dynamic landscape of corporate governance constantly evolving, mastering the art of conducting successful shareholder meetings in 2024 is essential for organizational success. In this guide, we will delve into the core components and strategies essential for orchestrating effective shareholder meetings, while adapting to the digital age and its complexities.
Use Lark Meetings to turn meetings into true collaborative experiences.
What is a shareholder meeting?
A shareholder meeting is a pivotal event where a company's management meets with its shareholders to discuss important decisions and developments within the organization. These meetings serve as a platform for shareholders to exercise their voting rights on essential company matters, providing a forum for open dialogue between the company's leadership and its stakeholders. Furthermore, they serve as an avenue for the company's board of directors to communicate the organization's performance, strategies, and challenges directly to its shareholders.
It is during these gatherings that shareholders are presented with essential information regarding the company's financial status, major developments, and future plans. This ensures that shareholders are well-informed about the organization's operations and can contribute effectively to its growth and direction.
Goals of shareholder meeting
The primary goals of shareholder meetings are as follows:
- Decision-making: Providing an opportunity for shareholders to vote on crucial matters such as the election of board members, executive compensation, and corporate actions like mergers and acquisitions.
- Transparency and Communication: Fostering open communication and transparency between the organization and its shareholders, ensuring that shareholders are well-informed about the company's performance, strategies, and challenges.
- Engagement: Encouraging shareholder engagement by allowing them to voice their opinions, ask questions, and express concerns about the company's governance and trajectory.
Who should attend shareholder meeting?
Shareholder meetings typically require the presence of the following participants:
- Shareholders: It is essential for shareholders to attend these meetings, as they exercise their right to vote and gain insights into the company's affairs.
- Board of Directors: The presence of the board is crucial as it lends credibility to the proceedings and enables direct communication with shareholders.
- Management Team: Their presence provides shareholders with insights into the operational aspects of the company, as well as reassurance about the direction of the organization.
Related:
Unlock the Power of Webinars: A Comprehensive Guide to Boost Your Business | Lark Blog | Lark BlogLearn more about Lark x Meetings
Topics, agenda, and structure of shareholder meeting
The agenda and structure of a shareholder meeting play a significant role in ensuring that it addresses the concerns and interests of the participants effectively. The following are key considerations to facilitate a well-structured meeting:
- Agenda Setting: Drafting a comprehensive agenda that includes essential company matters, such as financial reports, election of board members, voting on proposals, and addressing shareholders' concerns.
- Engagement Activities: Incorporating engagement activities, such as Q&A sessions, to encourage active participation and feedback from the shareholders.
- Timing and Logistics: Ensuring that the meeting is scheduled at a convenient time and location, integrating virtual participation where necessary, and providing clear instructions on how shareholders can participate remotely.
By meticulously planning the topics, agenda, and structure of the shareholder meeting, organizers can effectively address shareholders' concerns, establish clear communication channels, and navigate the meeting with efficiency.
Related:
Master the Art of Meeting Notes with Lark for Enhanced Collaboration | Lark Blog | Lark BlogLearn more about Lark x Meetings
How often does a shareholder meeting occur?
The frequency of these meetings varies as per legal and regulatory requirements and the organization's own policies. Most publicly traded companies conduct annual shareholder meetings to discuss matters such as electing directors and approving financial statements. However, special meetings may be called at any time to address specific critical matters.
Key differences between shareholder meeting and another similar meeting
The primary distinctions between a shareholder meeting and other corporate gatherings, such as board meetings, include:
- Stakeholder Engagement: A shareholder meeting typically focuses on engaging with shareholders, whereas a board meeting may be more focused on internal governance matters.
- Decision-Making Authority: Shareholder meetings provide an avenue for shareholders to exercise their voting rights, whereas board meetings are primarily for board members to deliberate and make decisions on operational and strategic matters.
Understanding these differences is crucial to ensuring that the objectives of each meeting are met effectively and in compliance with relevant regulations.
Learn more about Lark x Meetings
Examples of shareholder meeting
Example 1: annual shareholder meeting of xyz corporation
Example 1: annual shareholder meeting of xyz corporation
- In the annual shareholder meeting of XYZ Corporation, shareholders convened to vote on the re-election of board members, approve the company's financial statements, and provide feedback on the company's strategic direction.
Example 2: special shareholder meeting for merger approval
Example 2: special shareholder meeting for merger approval
- The special shareholder meeting was called to deliberate and vote on the proposed merger with a strategic partner. Shareholders were presented with detailed information about the potential merger and its implications on the organization's future.
Example 3: virtual shareholder meeting amid global pandemic
Example 3: virtual shareholder meeting amid global pandemic
- In response to the global pandemic, XYZ Corporation transitioned its annual shareholder meeting to a virtual format, ensuring that shareholders could participate and engage effectively despite the challenging circumstances.
Common pitfalls of a shareholder meeting
Running a successful shareholder meeting requires navigating various potential pitfalls, such as:
- Inadequate Preparation: Insufficient preparation can result in a lack of clarity, leading to disengagement from shareholders.
- Communication Challenges: Poor communication or an inadequate platform for virtual participation can hinder the effectiveness of the meeting.
- Legal and Compliance Risks: Failing to adhere to legal and compliance requirements can have repercussions on the validity of the meeting's decisions.
Mitigating these pitfalls is essential for ensuring a successful and productive shareholder meeting.
Learn more about Lark x Meetings
Dos and don'ts of a shareholder meeting
| Do's | Don'ts |
|---|---|
| Ensure clear communication | Avoid lack of preparation |
| Encourage engagement | Disregard stakeholder perspectives |
| Respect diverse viewpoints | Overlook regulatory compliance |
| Follow up on action items | Neglect post-meeting communication |
What makes a virtual shareholder meeting successful?
Virtual shareholder meetings require specific considerations to ensure their success, including robust technology infrastructure, clear communication channels, and efficient moderation to enable effective participation and decision-making.
Learn more about Lark x Meetings
Typical takeaways of the shareholder meeting
After a successful shareholder meeting, the following typical takeaways may occur:
- Resolution of Key Matters: Critical decisions on corporate matters, such as elections, approvals, and strategic initiatives.
- Enhanced Stakeholder Relations: Improved transparency, communication, and trust between the company and its shareholders.
Questions to ask in the shareholder meeting
The following are examples of questions that may be raised during a shareholder meeting:
- Financial Matters: Shareholders may inquire about the company's financial performance, outlook, and future investments.
- Strategic Direction: Questions related to the organization's future plans, including expansions, divestments, and market strategies.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mastering the art of conducting successful shareholder meetings is essential for organizations seeking to foster transparent governance, engage with stakeholders effectively, and make crucial decisions that steer the company's direction. By meticulously planning and executing these meetings, companies can build trust, instill confidence in their shareholders, and create a solid foundation for sustainable growth and success.
Q&A
When should a shareholder meeting be held?
A shareholder meeting is typically held annually, but special meetings may be called to address specific critical matters.
What are the typical items listed on the agenda for a shareholder meeting?
The agenda may include matters such as electing directors, approving financial statements, and voting on important proposals.
Is it mandatory for all shareholders to attend the meeting?
While attendance is encouraged, it may not be mandatory for all shareholders to attend the meeting. However, their participation is highly valuable.
How can a company ensure effective participation in virtual shareholder meetings?
Effective participation in virtual shareholder meetings can be ensured through clear communication, robust technology infrastructure, and efficient moderation of the proceedings.
Can a shareholder propose topics to be included in the agenda?
Shareholders usually have the right to propose topics to be included in the agenda, subject to the company's bylaws and regulatory requirements.
This comprehensive guide provides insights into orchestrating successful shareholder meetings in 2024, essential for fostering transparency, decision-making, and stakeholder engagement within organizations.
Use Lark Meetings to turn meetings into true collaborative experiences.
A Game Changer for Shareholder Meeting: Empower your team with Lark Meetings
In the fast-paced and dynamic world of modern business, effective communication and collaboration are crucial for success of Shareholder Meeting. Here we introduce Lark Meetings to serve as a centralized hub for all communication needs.
Transform your meetings into collaborative endeavors
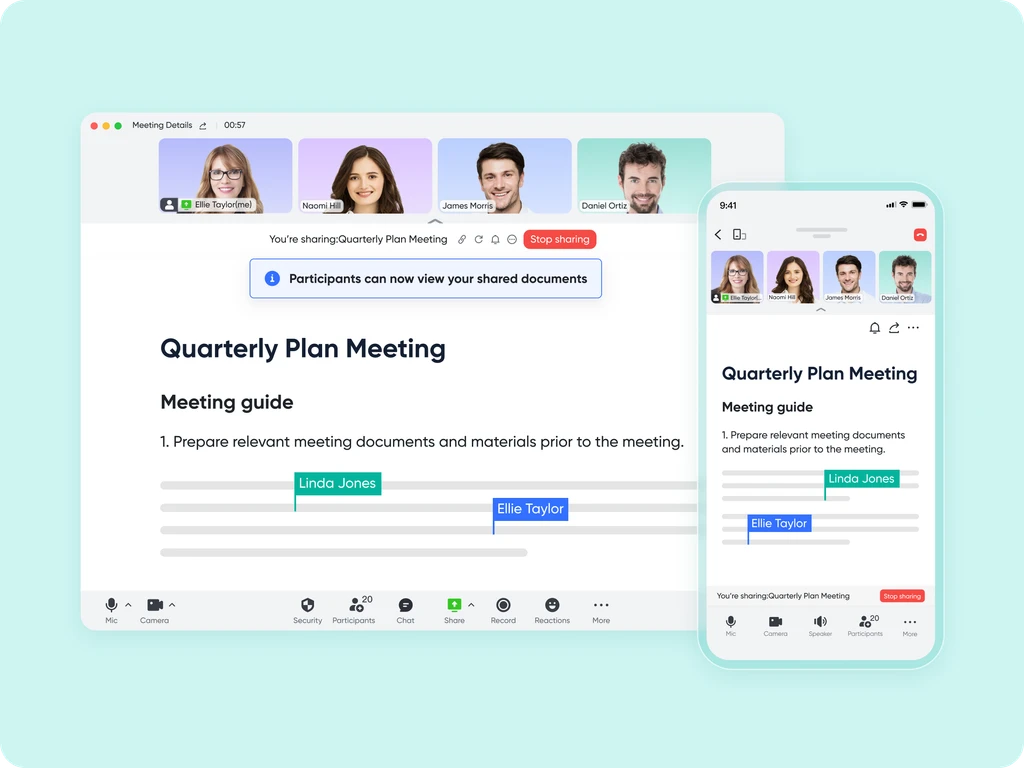
Leverage the potency of in-call document sharing, intelligent meeting minutes, and mobile-optimized features to enhance productivity collaboratively, irrespective of your location or schedule.
Seamlessly collaborate in real-time, across any device
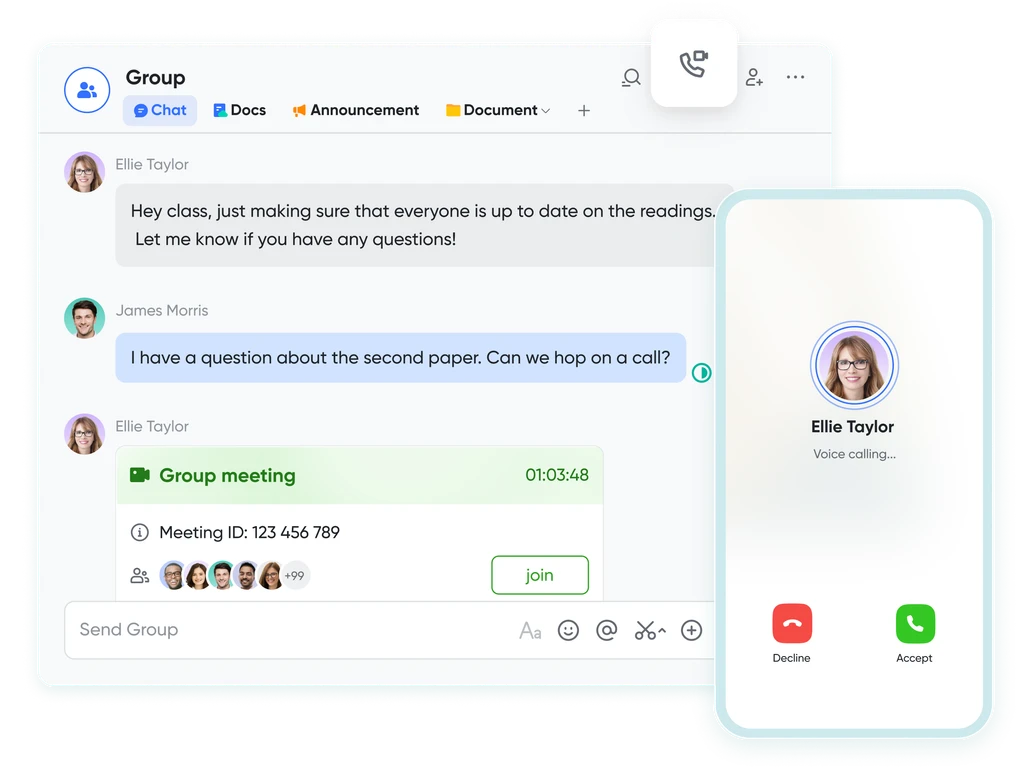
Share live documents instead of just screen views. Participants can navigate and edit simultaneously within the video call window, even while on the move.
Shift your focus to engagement, not note-taking
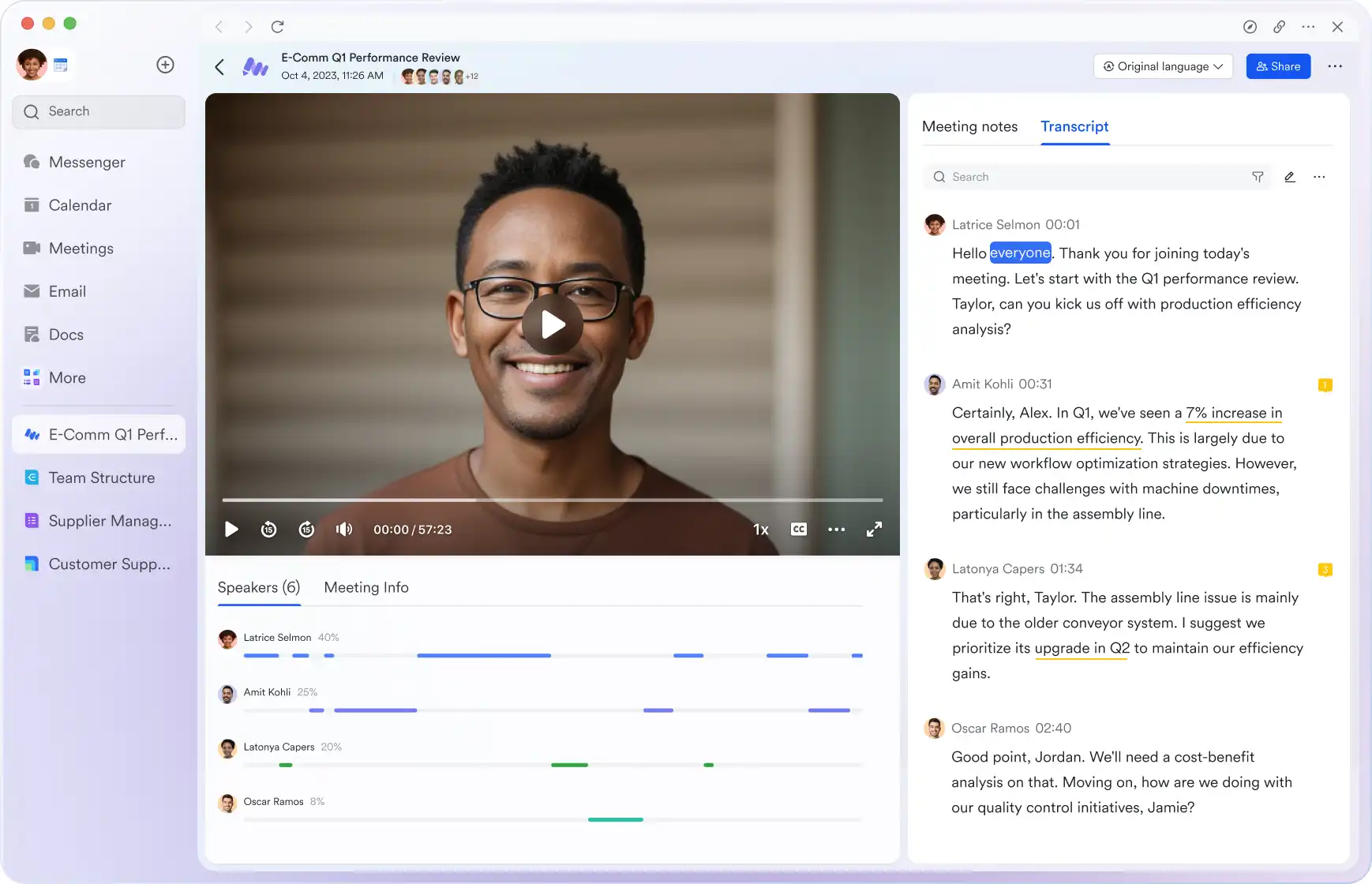
Lark Minutes automatically converts video meetings into transcripts, facilitating easy viewing, searching, and collaborative editing. Stay in the loop asynchronously, even if you can't attend the live meeting. Lark Minutes for meeting minutes support translation into 10+ different languages.
Break language barriers in communication
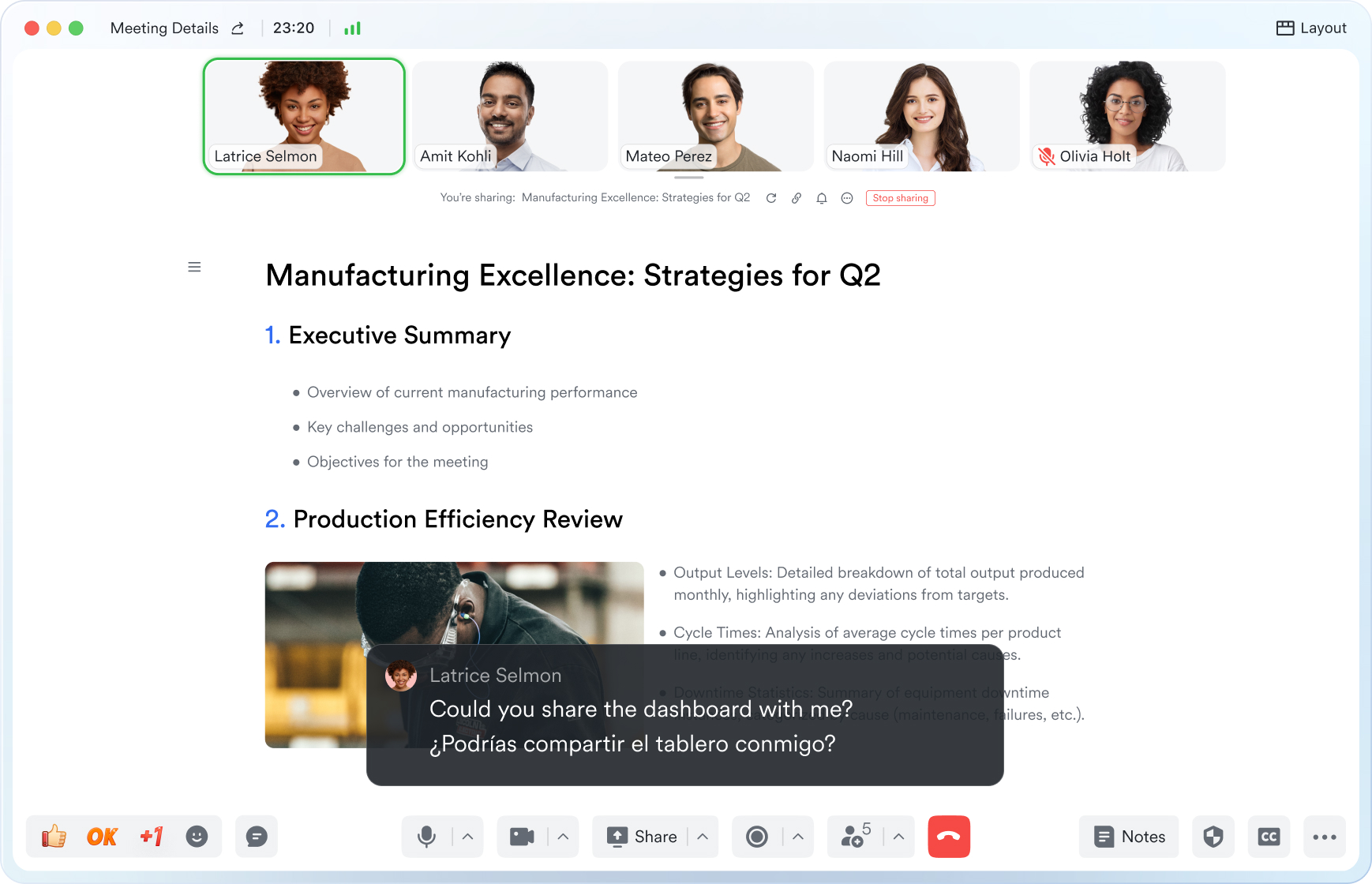
Lark Meetings provide real-time translation for subtitles, allowing individuals from diverse backgrounds to express themselves in their native languages. Ensure every voice is heard, regardless of geographical location. Live subtitles currently support translations from English, Chinese, and Japanese to 10+ different languages. See more translation feature in Lark.
Connect with larger audiences
Host dynamic online meetings and events accommodating up to 1,000 participants, with the flexibility of up to 50 breakout sessions for intimate group discussions within the larger meeting context. Try more Lark features for free.








